The greenhouse effect and its consequences – Investigating global warming
In this set of three activities, students will do hands-on experiments and learn how to interpret satellite images for better understanding the overall effects of global warming. In activity 1 students will make a model to demonstrate the greenhouse effect by showing that a higher level of carbon dioxide (CO2) means a higher temperature. The experiment will be complemented by the interpretation of satellite images showing the Earth’s CO2 levels at different time periods. Students will then learn about some of the consequences of an increased greenhouse effect – ice melting and changing albedo values. Students will explore these topics in activities 2 and 3.
Subject Geography, Physics, Science
- What the greenhouse effect is and how human activity changes the energy balance in Earth’s atmosphere
- The potential effects of increased levels of carbon dioxide on the Earth’s climate
- Possible consequences of the increased greenhouse effect
- The different consequences of flooding and rising sea water level due to melting sea-ice and melting ice sheets and glaciers
- What albedo is and how the reflectivity of different surfaces affect temperature
- How Earth observation can be used to monitor Earth’s climate
- 2 1L flasks
- Corks with hole for holding the thermometer
- 1 lamp with a heating bulb (more than 100W)
- 2 thermometers (0.10C precision)
- Acetic acid 32%
- Baking powder
- Ice cubes (optional)

- 4 glass beakers 250 ml
- Metal net with a diameter slightly bigger than the beakers
- Coloured ice cubes
- Table salt (NaCl)
- Tea-spoon or spatula to stir with
- Marker pen
- Timer
from surfaces of different colours affects temperature by doing a hands-on experiment. Students will understand that the reflectivity of different surfaces, their albedo, plays an important role in the Earth’s climate. They will investigate the following questions:
1) How does colour influence the temperature of the surfaces?
2) How does the wind and humidity affect the albedo and thus the temperature of the surface measured?
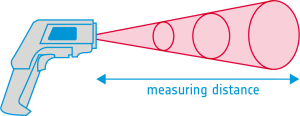
- IR-thermometer
- Pieces of paper or cardboard with different grey tones and different colours (see annex II)
- Lamp with heat bulb (if not sunny)
Did you know?
EarthCARE is an ESA mission that will improve our understanding of the role that clouds and aerosols play in both reflecting solar radiation back into space and trapping infrared radiation emitted from Earth’s surface. EarthCARE – the Earth Cloud Aerosol and Radiation Explorer – is being developed in collaboration with ESA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, JAXA. EarthCARE will collect global observations of cloud and aerosol profiles together with solar and thermal radiation to include these parameters in numerical weather and climate models. In addition, EarthCARE aerosol data will be valuable for monitoring air-quality.

Biodiversity and Habitat Loss
Brief description In this set of three activities, students will start with a reading assignment that introduces vocabulary and ideas...
Astro farmer
Brief description:In this set of six activities, students will investigate which factors affect plant growth, and relate these factors to...
Is ozone good or bad? -The discovery of the Antarctic ozone hole
Brief description In this set of three activities, students will learn about ozone and the impacts – good and bad...
The ice is melting – How can we investigate the effects of melting ice?
Brief description In this set of four activities, pupils will explore the impacts of global warming and melting ice on...
Highways of the Oceans – Sea currents and the connection to climate
Brief description In this set of three activities, students will use an multimedia module to learn about sea currents, the...