Planetary Heat Pumps
In this set of three activities, students will learn how ocean circulation has an impact on climate. In the introductory activity, they carry out calculations to compare the relative impact of global warming on the atmosphere and oceans. A practical activity using readily available equipment allows students to see how water of different temperatures can form layers in the ocean and to consider how they might use this to explore the effect of changes in salinity. In the final activity, students use the Climate from Space web application to find out more about the Gulf Stream.
Subject Geography, Science, Earth Science
- Carry out calculations to compare the role of the oceans and atmosphere in regulating the climate
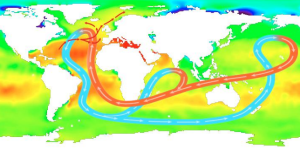
- Explain how the global thermohaline circulation arises
- Describe how ocean currents transport water and energy around the Earth
- Use a model to examine the movement of water of different temperatures and explain stratification in the ocean
- Design practical methods of investigating a question about how water moves in the oceans
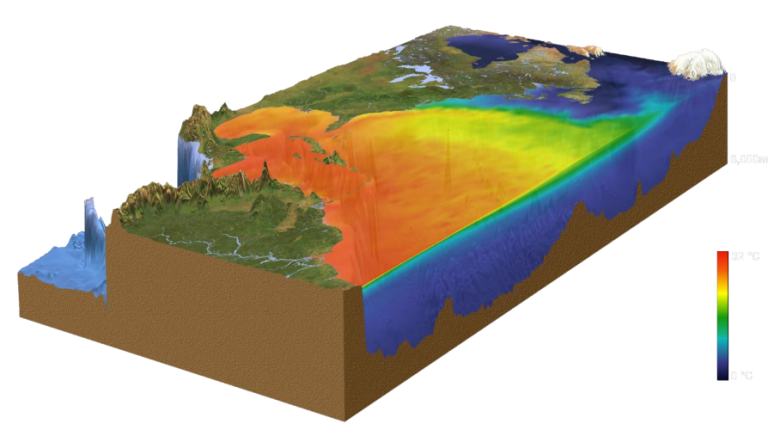
- Describe the behaviour of the Gulf Stream using information from climate data
- Synthesise data from records of at least two essential climate variables to explain an observed correlation or trend
- Large transparent container per group
- Small container per group to submerge in the larger container
- Plastic bags
- Rubber bands or string
- Food colouring or ink
- Ice in a bucket for cooling, or refrigerated water
- Access to hot and cold water
- Stopwatch or clock per group (optional)
- Camera or smartphone per group (optional)
- Thermometers (optional)
- Cloths or paper towels
- Student worksheet 2 (2 pages)
- Materials for creating posters, or software for creating videos or presentations
- Climate from Space online resource: Planetary Heat Pumps story (optional)
Did you know?
Before the age of satellites, the temperature of the ocean could only be measured using thermometers linked to the shore, lowered from ships, or attached to buoys or submersibles. This, of course, meant that measurements were patchy and there were continuous records for very few places. Thermal cameras on satellites can detect the surface temperature of the ocean across the whole world at regular intervals. A satellite in geostationary orbit can view each section of the sea in a particular hemisphere once every fifteen minutes or so; one in a polar orbit, closer to the Earth, can see more detail and cover the entire planet but will only measure the temperature at a particular place every ten days or so.
Paxi explores wind
Brief description: Learn about wind, what causes it and how and why we study it in the latest Paxi adventure...
Highways of the Oceans – Sea currents and the connection to climate
Brief description In this set of three activities, students will use an multimedia module to learn about sea currents, the...
Country under Threat – The prospects for life on small islands
Brief description In this set of four activities pupils will learn about the causes and potential impacts of sea-level rise...
The ice is melting – How can we investigate the effects of melting ice?
Brief description In this set of four activities, pupils will explore the impacts of global warming and melting ice on...
Sea ice from space – Investigating Arctic sea ice and its connection to climate
Brief description In this set of three activities, students will investigate Arctic sea ice. First, they will perform a hands-on...


