Climate Detectives Projects 2020-2021
Project title: Forest in Change
Team: Earth Protectors, “Erdschuetzlinge”
Gymnasium Waidhofen an der Thaya Waidhofen an der Thaya Austria 24 19Student’s age: 14-15 years old
How big is the spatial distribution of forest damage in the spruce and pine stand by the bark beetle in the Waldviertel region (Waidhofen an der Thaya and Zwettl district, Lower Austria) for the period 2017 to 2020 due to longer periods of drought and global warming in the region?

Climate change is also making a strong impact on bark beetles in the Waldviertel region (NW of Lower Austria). The heat and dryness are optimal for the bark beetle expansion. Secondly there are spruce monocultures in this area, which are not in accordance with the location, where bark beetle can increase rapidly.
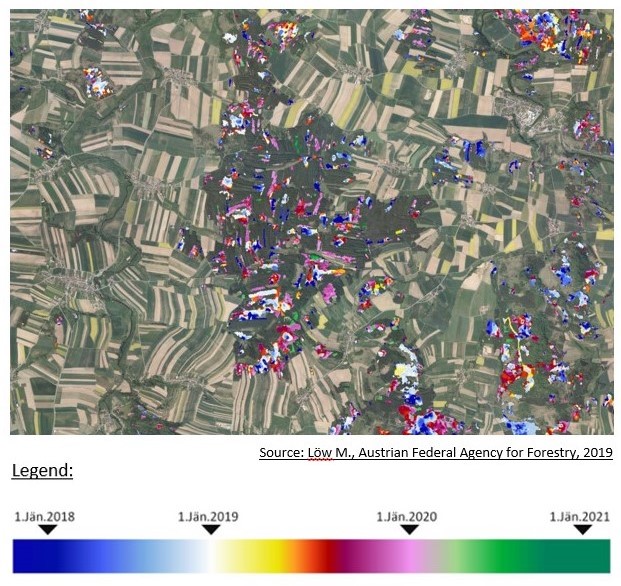
In case study areas (Buendlberg, Military Training Area near Alltensteig and the forest NE of Waidhofen an der Thaya) the dissemination of bark beetle in time and space can be investigated by ESA-Sentiel 2 ifrared satellite images. Affected forstest areas show red-brown anomalies.
The Austria Federal Agency for Forest is developing a suitable method in remote sensing to quantify the affected areas by overlaying Ortho Photos and ESA-Sentiel 2 Images. Because of new methods in remote sensing it is possible to quanifiy the damage and forest owners will get financial aid e.g. also to develop the forest monocultures to nature-orientated sustainable forest which can survive in climate change.

Since 2015, the bark beetle phenomenon has been multiplying rapidly. Another reason for that is, for example, that spruce trees are planted in large areas and the bark beetle has so much attack surface. Particularly, the Waldviertel and the Muehlviertel region (Austria) are strongly affected by the bark beetle plague.
Archaeology offers chronic examinations. In the early Middle Ages there were mainly a mixed natural wood with mostly beeches and fir dominant in the Waldviertel region (Lower Austria).
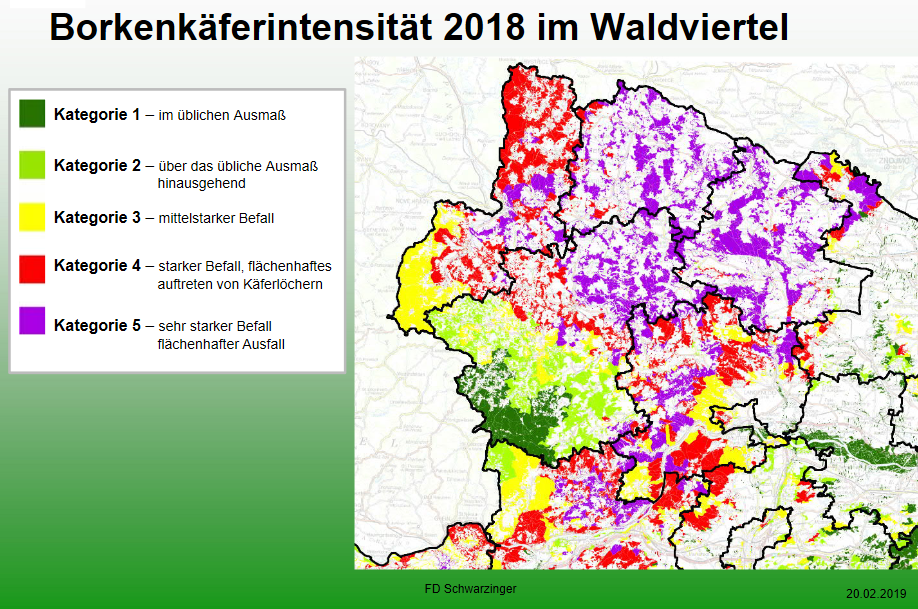
In the last few years the forests were heavily infested by the bark beetle in the region Waldviertel (Austria). The special ‘bark beetle years’ were 2018 and 2019, a little weakened in 2020. The tree species mostly infested is the spruce. Also pine trees are often infested. Spruces aren’t going to be planted anymore in the Waldviertel region in the future. Instead, larch, marple, oak, European beech and many other species will be used, because deciduous trees are not attacked. It is set to mixed forests.
The damage caused by the insects has fallen since then, but still above average.
The Austrian bark beetle monitoring was initiated in 2005 by the state forestry authorities and the forestry board of the Chamber of Agriculture. The aim of this service is to inform farmers and foresters, who suffer from a bark beetle plague, about the current flight situations of the most stubborn bark beetle species. These can then set up bark beetle traps to prevent the greatest possible damage.
The forest has already mostly been destroyed In the district Waidhofen an der Thaya an Zwettl (NW of Lower Austria). An impressive example is the area of Raabs an der Thaya. Also the forest is destroyed in the military training area near Allentsteig. The spruces and pine trees which are still left are highly threatened.
BRUENDLBERG:
In 2018 there were around 50,000 solid cubic meters of firewood in the district of Waidhofen an der Thaya. The federal state of Lower Austria promised 1 million euros for immediate action against the bark beetle.
In December of 2020, over 1,000 trees were planted in the area of the Bruendlberg, for example sweet chestnut, sun linden tree, redwood trees and many more.
MILITARY TRAINING AREA ALLENSTEIG:
About 80 percent of the spruce stand is infested or already destroyed. The beetle raged on the 7,900 hectares of forest and entire areas were bare. In 2018 the mark of 200,000 solid cubic meters of timber was reached. That is more than six times the usual annual yield.
In order to transport the wood out of the dud area, forest workers are out and about with the splinter-proof harvester. No classic spruce monocultures are replanted.
Before the actual work of the harvesters can start, a surface search must be carried out. Not only do duds appear, but around 100 relics are found every year. To ensure that the dead wood comes out of the forests, around 400 trees are cut and loaded every hour. 150 truckloads left Allentsteig every week.
Individual trees stand out that have withstood the bark beetle. Experts want to take a closer look at the genetics of these trees.
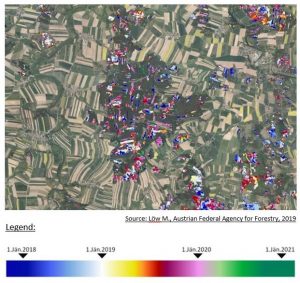
The Austrian Federal Agency for Forestry is developing a special remote sensing method in combining ESA-Sentiel 2 satellite images and ortho photos for quanitfiying the forest damage because of the barke beetle. Since 2021 there will be paid financial subsidies to forest owners to redevelop the forest to nature-orientated sustainable forest which can survive in climate change.
There is an overview of any actions the team ‘Earth Protectors’ has taken or plan on taking to help address the climate problem they investigated:
• save water
• make a shopping list before going to shop, don’t waste food
• buy organic products
• buy regional products
• rely on a vegetarian diet and no industrial treatment
• buy Fair Trade products
• plant your own vegetable garden
• flowering meadows in the garden instead of a lawn
• later mowing of flowering meadows in the garden
• go by foot more
• more cycling
• use the public transport instead of taking the car
• don‘t drive unnecessary routes with the car
• use reusable shopping bags
• buy second hand products
• don’t buy clothes that you don’t need
• donate clothing for second hand
• use less plastic
• don’t buy products with animal testing
• repair instead of buying new products
• dispose trash appropriately (waste separation)
• use recyclable glass bottles instead of plastic bottles
• rely on renewable energy (in the household)
• stay on the paths in the forest and don’t disturb wild animals
• donate money for environmental protection campaigns
Projects are created by the teams and they take the full responsibility of the shared data.
← All projects