Climate Detectives Projects 2020-2021
Topics
Project title: Climate change and rainfall
Team: The rain
ITIS E. Barsanti ISIS E. Europa Pomigliano D’Arco Italy 25 11Student’s age: 14-15 years old
How do we prevent flooding problems affecting the areas in which we live?

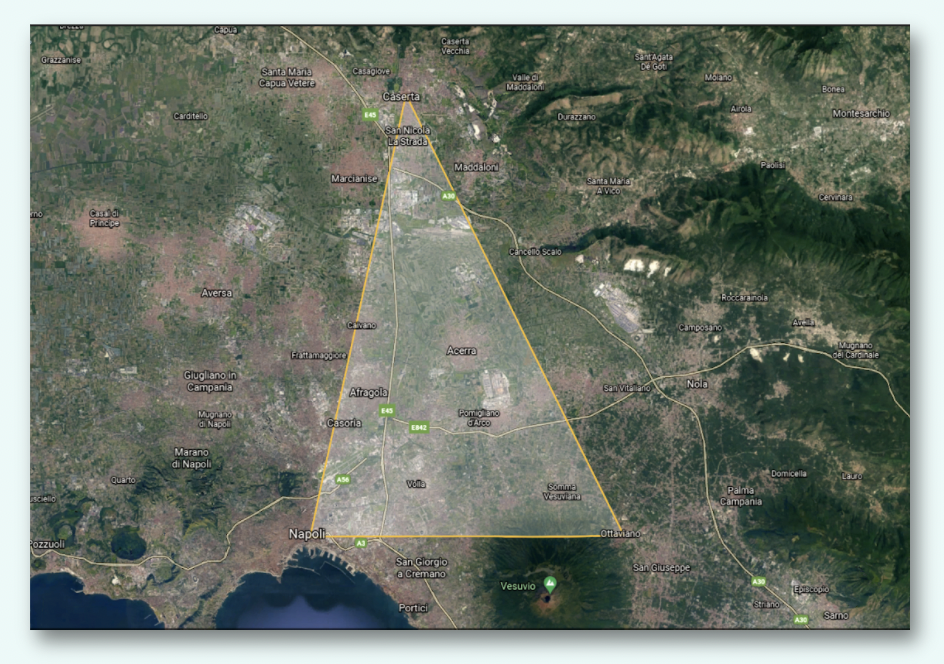
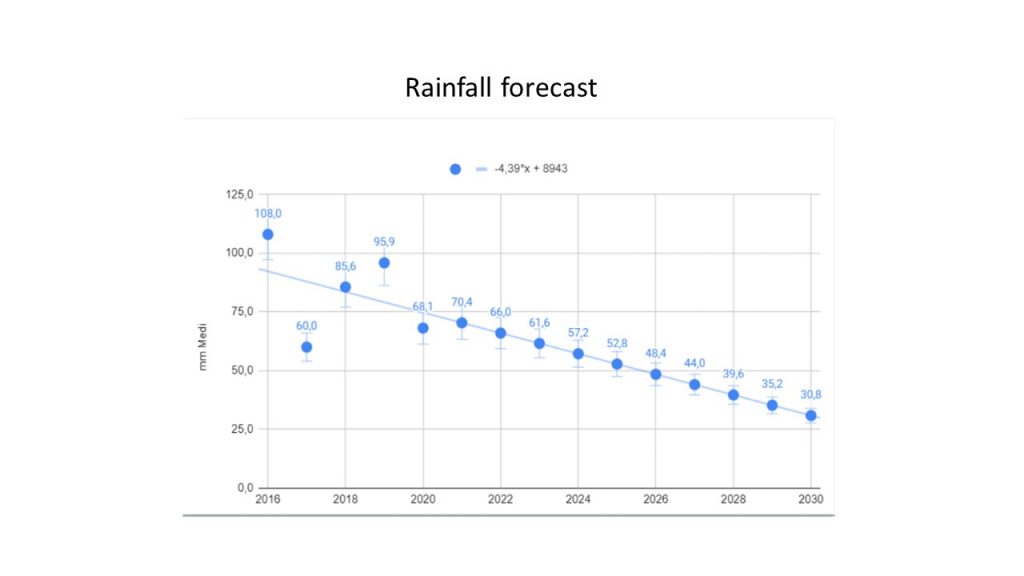
Students, from ITIS E. Barsanti and ISIS Europa, located in Pomigliano d’Arco, near Naples work together combining Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) and Nature Based Solution (NBS) .They observing whether of our country, a small town located 37m above sea level with a warm and temperate climate. Rains were abundant and frequent in November and December by analyzing data collected by our meteorological station. In the last 15 days of december 101.1mm rain fell, the same of last year determining flooding due to inadequacy collection systems. The excess flow rates discharged to the surface by the pressurized sewer can fill any depressions on the ground, or flow through preferential routes, creating a flow network that in urban areas affects roads, sidewalks, natural depressions and small streams . The intense rainfall increases hydraulic risk generated which impact on people and infrastructures. The students understood that reduction of permeable areas – reduction of vegetated areas – reduction of surface reservoirs is the problem. Through google earth and eurostat.eu, analyze the artificial, waterproofed areas and agricultural surfaces present nearby school. The hydrological balance in natural conditions (P = ET + R + I) Based on the rainfall data by Ance Campania during 2021, the pupils make future predictions of precipitation in the our town with the triangulation method and the “Shape ”Of Google Earth. The three localities were: Naples Camaldoli, Ottaviano and Caserta, and with the “geometric” center of gravity of this triangle it was possible to roughly estimate the margin of error.

Highlights how the transition from agricultural land (natural cover) to a completely waterproofed surface (square, asphalted and / or cemented road, etc.) leads to a progressive reduction of the infiltration coefficient c. the. (represented by the amount of water that infiltrates in conjunction with a meteoric precipitation) and an increase in the surface runoff d.s. (part of precipitation flowing to the surface).
Example of calculation
Asphalted surface – schoolyard c.i. = 15% d.s. = 55% (with peaks of up to 80%).
Agricultural land – adjacent cycle path c.i. = 50% r.a. = 10%
The increase in the size of surface runoffs is evident where the soil has been replaced by impermeable areas. It should be borne in mind that during particularly intense hourly rainfall (in the order of 70-80 mm / h) the urban drainage system can go into crisis, causing localized flooding that seriously impacts anthropogenic structures. The forecast implies that the amount of water that will fall in the coming years will be less and less, despite the damage from flooding, floods … have been growing in recent times.
We can give an explanation to all this, saying that on days when it rains, the rain is very intense, which cannot be disposed of by the current sewage works.

By use NBS methodology elaborate a project on infrastructures, correlating nature and urban environment. The idea is create urban drainage channels to drain excess rainwater along the edges of the roads . This system require: limited number of components ,is easy to install and adaptable in length, easily removable and maintenance , stay level with the ground. This solution avoid flooding and drain rainwater to other areas.The students identified possible materials to make water drainage channels which are: galvanized steel, cast iron, polymer, PVC . The materials must be able to withstand the load, and the stresses caused by frequent passage of vehicles, temperature changes and resistance to chemicals. They calculated the water flow rate based on the size of the drainage channels by asking themselves questions
How much rainwater passes inside the channel in a given period of time? What is the slope of the surface or the slope of the channel itself? How important are the dimensions and the grille of the drain?
The volume of rainwater that passes inside the channel is calculated on the basis of the area the runoff coefficient, on an annual basis which expresses the permeability of the surfaces. For examples: soils such as agricultural areas and meadows have a lower coefficient, around 0.10-0.15, since they absorb water more easily, while for asphalt it reaches 0.85- 1.00 precisely because of its poor permeability;rainfall intensity expressed in millimeters per hour.
A calculation of the volume of rainwater (the Rational Method) is therefore:
V = BxIcrxA / 3600
https://climateandrainfall.blogspot.com/
Projects are created by the teams and they take the full responsibility of the shared data.
← All projects